Why is the Earth moving away from the Sun? Understanding the Astronomical Phenomenon
March 31st, 2025The Earth is Moving Away from the Sun: Understanding the Astronomical Phenomenon
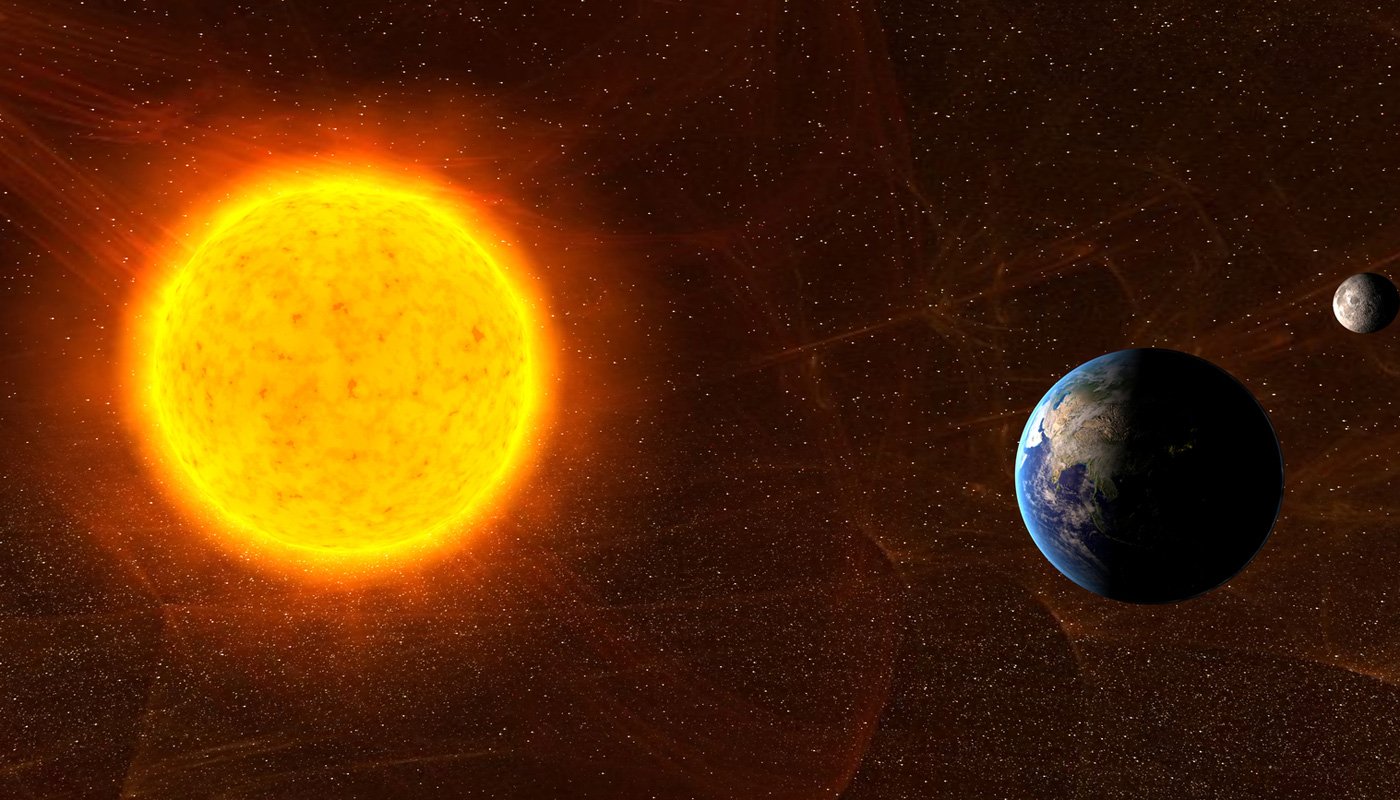
The Earth is gradually moving away from the Sun, a process that takes place over millions of years. This astronomical phenomenon is the result of a series of interconnected factors, involving both the physics of stars and the gravitational interaction between bodies
Why is that?
The main reason for this gradual drift is the Sun's loss of mass. Through nuclear fusion, the Sun transforms hydrogen into helium, which results in the emission of energy. This constant loss of mass reduces the Sun's gravitational pull on the Earth. Consequently, the gravitational pull decreases, allowing the planet to slowly move away.
In addition, just as the Moon causes tides on Earth, the Earth also generates tides on the Sun. These "solar tides" are caused by the gravitational attraction of the Earth on the mass of the Sun. This movement creates friction and resistance, which slow down the Sun's rotation. The deceleration of the Sun's rotation results in the transfer of angular momentum from the star to the planet, contributing to the gradual moving away of the Earth.
The Absentee Rate
Studies indicate that the Earth is moving away from the Sun at a rate of approximately 15 centimeters per year. Although this rate is small, it has significant long-term implications, affecting the dynamics of the Solar System. This process is part of the natural cycle of evolution of the Solar System, which takes place over billions of years.
Future consequences
Although the drift is a very slow process, in the long term it could have an impact on life on Earth. If this drift continues, one day there could be a change in the Earth's climate, as the amount of solar radiation received by the Earth will decrease. However, this event is very far in the future, and scientists are still studying the deeper implications of this change.
The Role of Gravity and Tides
Solar tides play a fundamental role in this distancing. The interaction between the Earth's gravity and that of the Sun creates a tidal phenomenon on the Sun, which results in friction. This friction is responsible for slowing down the Sun's rotation, which in turn affects the Earth's orbital movement.
The gradual moving away of the Earth from the Sun is an example of how celestial bodies are in constant motion, interacting with each other in complex ways. Understanding these processes is essential for deepening our knowledge of the evolution of the Solar System and the conditions that could affect the habitability of our planet.
Impact on the Solar System
This gradual drifting away is not an isolated phenomenon; it is closely linked to the evolution of the Solar System as a whole. As the Earth moves away from the Sun, this can alter the stability of the planets' orbits and eventually affect the formation of new stars and planetary systems.
Understanding these processes helps scientists predict future events and better understand the fate of the Solar System, as well as the potential habitability of other planets in distant star systems.
Conclusion
Although the Earth's retreat from the Sun is a natural and gradual phenomenon, it helps us to better understand the interactions in the Solar System. Although this process has no immediate impact, it is a reminder of how astronomical forces shape our planet and how the future of the Earth is closely linked to the behavior of the Sun. Discoveries about this separation may also help predict changes in our environment, offering new perspectives on the evolution of life on the planet.